Configure Postfix to Send Email Using External SMTP Servers
Traducciones al EspañolEstamos traduciendo nuestros guías y tutoriales al Español. Es posible que usted esté viendo una traducción generada automáticamente. Estamos trabajando con traductores profesionales para verificar las traducciones de nuestro sitio web. Este proyecto es un trabajo en curso.
NoteThis guide was originally written for Debian 7. It has since been tested to work with Debian 9.
You may want to configure Postfix to use an external SMTP provider like Mandrill, and SendGrid so you no longer have to build, maintain, and scale your own SMTP relay server. Another reason is to avoid getting your mail flagged as spam if your current server’s IP has been added to a spam list. This guide shows you how to configure Postfix to use an external SMTP provider and also shows specific examples for Mandrill, and SendGrid. However, you can apply the steps in this guide to configure Postfix to use any external SMTP provider.


This guide may involve or result in sending email. In an effort to fight spam, Linode restricts outbound connections on ports 25, 465, and 587 on all Linodes for new accounts created after November 5th, 2019. For more information, please see Sending Email on Linode.
What is Postfix Used For?
Postfix allows you to route and deliver emails and uses the Simple Mail Transfer Protocol (SMTP).
What is the Postfix Configuration Process?
The majority of the Postfix configuration process is completed in the main.cf and master.cf files that are located in the /etc/postfix/ directory. The /etc/postfix directory is available once you have installed Postfix on your Linux system.
At a high-level Postfix configuration involves the following steps:
- Gather prerequisites, which include a fully qualified domain name(FQDN), updating your system, and installing the
libsasl2-modulepackage - Install Postfix on your system
- Configure SMTP usernames and passwords
- Secure your password and hash database files
- Configure the relay server
- Test your Postfix configuration
- Set up Postfix with Mandrill, and SendGrid
Postfix Configuration
NoteIf you’re using Gmail or Google Workspace, see our Configure Postfix to Send Mail Using Gmail and Google Workspace on Debian or Ubuntu guide instead.
Gathering Prerequisites
In this section, you complete all prerequisite steps to configure Postfix to use an external SMTP server. Prerequisites to configure Postfix using an external SMTP server are:
Ensure you have fully qualified domain name (FQDN). The Fully Qualified Domain Name (FQDN) is the absolute domain name, including subdomains, top-level domain, and root zone, that will direct queries under the Domain Name System (DNS) to an exact location—in this context, to your Linode. For a detailed explanation, see What is FQDN For? Linode Community Q&A.
Ensure your system is up-to-date:
apt-get update && apt-get upgradeInstall the
libsasl2-modulespackage:sudo apt-get install libsasl2-modules
Your system is now ready to install Postfix.
Installing Postfix
Install Postfix by running the following command:
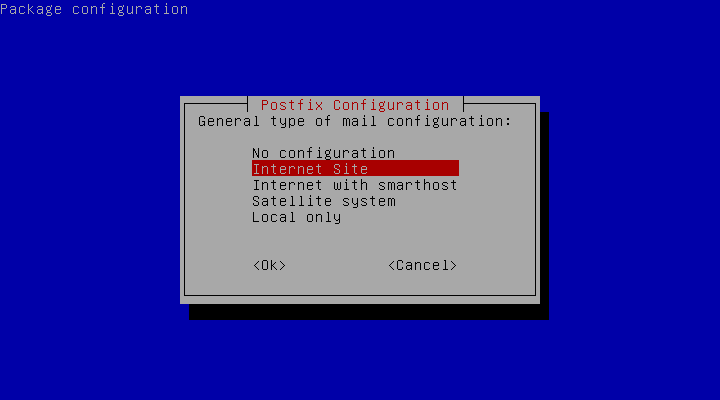
sudo apt-get install postfixYou receive a prompt asking for your General type of mail configuration. Select Internet Site from the options.
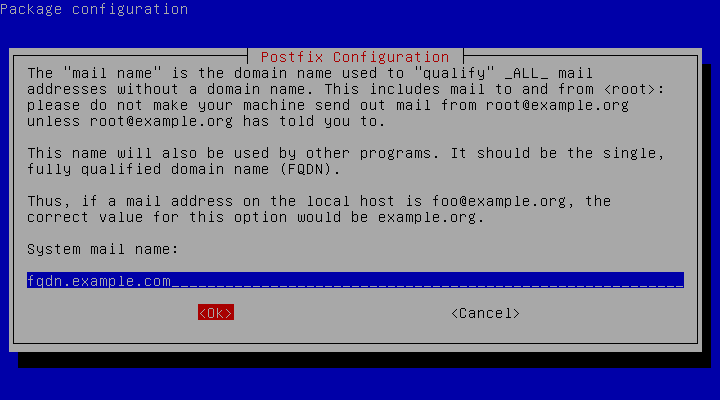
- Enter your fully qualified domain name when asked for your System mail name. An example FQDN is fqdn.example.com.
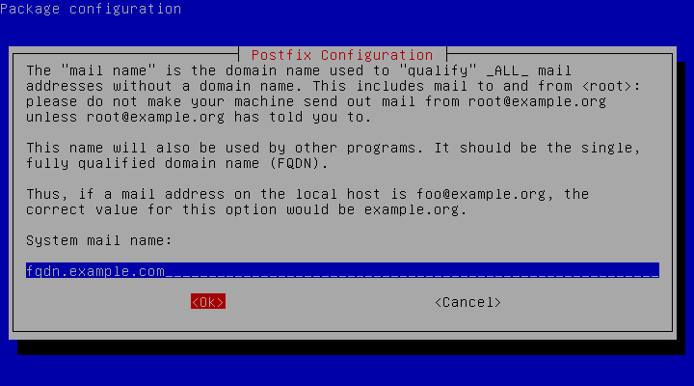
Once the installation is complete, open the
/etc/postfix/main.cffile using your preferred text editor. Edit the file to add your Linode’s FQDN to the myhostname configuration, if it is not already configured, and save your changes.- File: /etc/postfix/main.cf
1myhostname = fqdn.example.com
Configuring SMTP Usernames and Passwords
Usernames and passwords are stored in the /etc/postfix/sasl_passwd file. In this section, you add your external mail provider credentials to the sasl_passwd Postfix configuration file.
NoteThe examples in this section provide the general steps to configure Postfix to use an external SMTP provider. If you want to use Mandrill or SendGrid as your SMTP provider, you can refer to the examples in the Postfix Configuration with Mandrill, and SendGrid section of this guide.
First, open or create the /etc/postfix/sasl_passwd file:
Using a text editor of your choice, open the
/etc/postfix/sasl_passwdfile. If it does not yet exist, create it.Add the example line to your
sasl_passwdfile and replaceusernameandpasswordwith your SMTP provider credentials.- File: /etc/postfix/sasl_passwd
1[mail.isp.example] username:password
Create a Hash database file for Postfix using the
postmapcommand. This command creates a new file namedsasl_passwd.dbin the/etc/postfix/directory.sudo postmap /etc/postfix/sasl_passwd
Secure your Password and Hash DB files
In the previous section you added plain text credentials to the /etc/postfix/sasl_passwd and /etc/postfix/sasl_passwd.db files. For this reason, you have to change the each file’s permissions to restrict access to all users other than the root user.
Run the following command to change your each file’s permissions:
sudo chown root:root /etc/postfix/sasl_passwd /etc/postfix/sasl_passwd.db sudo chmod 0600 /etc/postfix/sasl_passwd /etc/postfix/sasl_passwd.db
Configuring the Relay Server
You are now ready to provide the configurations needed by Postfix to use the external SMTP server. This configuration tells Postfix to deliver mail indirectly via a relay host, which in this case, is an external SMTP server.
NoteRefer to the Postfix Configuration with Mandrill, and SendGrid section of this guide for specific relay host configurations for Mandrill, and SendGrid.
Using a text editor, open the
/etc/postfix/main.cffile.Update the
relayhostconfiguration with your external SMTP relay host. Replacemail.isp.examplewith your provider’s information. If you specified a non-default TCP port in thesasl_passwdfile, then use the same port when configuring the relay host. The example uses587as its port number.- File: /etc/postfix/main.cf
1 2# specify SMTP relay host relayhost = [mail.isp.example]:587
Add the end of the file, add the example file’s parameters to enable authentication and save the changes you made to your
main.cffile.- File: /etc/postfix/main.cf
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10# enable SASL authentication smtp_sasl_auth_enable = yes # disallow methods that allow anonymous authentication. smtp_sasl_security_options = noanonymous # where to find sasl_passwd smtp_sasl_password_maps = hash:/etc/postfix/sasl_passwd # Enable STARTTLS encryption smtp_use_tls = yes # where to find CA certificates smtp_tls_CAfile = /etc/ssl/certs/ca-certificates.crt
Restart Postfix to enable your configurations:
sudo service postfix restart
Testing Your Postfix Configuration
You can now test your Postfix Configurations by using your system’s mail utility.
Install the
mailutilspackage to use themailutility.sudo apt-get install mailutilsCompose an email to verify that your system is able to successfully send it. Replace the email address with your own and your intended recipient’s email address.
echo "body of your email" | mail -s "This is a subject" -a "From:you@example.com" recipient@elsewhere.comNote
You can use Postfix’s own Sendmail implementation to test your Postfix configuration. Replace the example’s values with your own. When you are done drafting your email type ctrl d.
sendmail recipient@elsewhere.com From: you@example.com Subject: Test mail This is a test email
Postfix Configuration with Mandrill, and SendGrid
This section shows you settings for some popular mail services you can use as external SMTP servers. You may have to do some fine-tuning on your own to avoid Postfix logins being flagged as suspicious.
Postfix Configuration for Mandrill
Open your
/etc/postfix/sasl_passwdfile and replaceUSERNAMEandAPI_KEYwith your own Mandrill credentials and save your changes.- File: /etc/postfix/sasl_passwd
1[smtp.mandrillapp.com]:587 USERNAME:API_KEY
Open your /etc/postfix/main.cf file and add the Mandrill relay host information included in the example file.
- File: /etc/postfix/main.cf
1relayhost = [smtp.mandrillapp.com]:587
Create a hash database file for Postfix using the
postmapcommand:sudo postmap /etc/postfix/sasl_passwdRestart Postfix to enable your new configurations:
sudo service postfix restart
Postfix Configuration for SendGrid
Open your
/etc/postfix/sasl_passwdfile and replaceUSERNAMEandPASSWORDwith your own SendGrid credentials and save your changes.- File: /etc/postfix/sasl_passwd
1[smtp.sendgrid.net]:587 USERNAME:PASSWORD
Open your /etc/postfix/main.cf file and add the SendGrid relay host information included in the example file.
- File: /etc/postfix/main.cf
1relayhost = [smtp.sendgrid.net]:587
Create a hash database file for Postfix using the
postmapcommand:sudo postmap /etc/postfix/sasl_passwdRestart Postfix to enable your new configurations:
sudo service postfix restart
How Do I Check My Postfix Configuration?
All Postfix configuration files are stored in the /etc/postfix directory. You can use the postconf command to view all of your system’s Postfix configurations and their details. This is a great way to verify that your Postfix configuration values are as you expect them to be.
To view all the available postconf options, view its manual pages using the man postconf command.
How Do I Change My Postfix Configuration?
Postfix configuration files are located in the /etc/postfix/ directory. Most of your configurations are made in either the main.cf or master.cf files. To learn more about Postfix configuration files see
Postfix’s README.
This page was originally published on