Installing Canvas on Ubuntu 20.04
Traducciones al EspañolEstamos traduciendo nuestros guías y tutoriales al Español. Es posible que usted esté viendo una traducción generada automáticamente. Estamos trabajando con traductores profesionales para verificar las traducciones de nuestro sitio web. Este proyecto es un trabajo en curso.
Canvas is a popular learning management system (LMS) noteworthy for its modern design and ease of use. Canvas provides a comprehensive website for education and training courses, whether those courses are in-person, online, or a mix of the two. Moreover, Canvas is open source. You can freely download and install an instance on your server, giving you a higher degree of control than with a hosted LMS.
This guide shows you how to get a Canvas website up and running on an Ubuntu 20.04 server.
Before You Begin
If you have not already done so, create a Linode account and Compute Instance. See our Getting Started with Linode and Creating a Compute Instance guides.
Follow our Setting Up and Securing a Compute Instance guide to update your system. You may also wish to set the timezone, configure your hostname, create a limited user account, and harden SSH access.
Prepare an SMTP server that Canvas can use to send email notifications to users. You can use a third-party SMTP service for this purpose. This guide’s example configurations use Mailgun as the third-party SMTP provider.
You can, alternatively, create your SMTP server by following the Email with Postfix, Dovecot, and MySQL guide. However, because of Canvas’s resource demands, you may want to run the SMTP server on a separate machine than the one running Canvas.
Canvas recommends a minimum of 8 GB of RAM. The website may operate with fewer, but doing so may result in installation and/or runtime issues. This is especially the case when all of the Canvas components are running on a single machine.
You can run some of the components of your Canvas installation on separate machines to improve performance if needed. Refer to Canvas’s Production Start guide for more on what components can be installed independently. Be aware that this approach requires some additional configuration to enable communications between the components.
Replace
example.comin this guide with your server’s domain name. You can complete the Add DNS Records steps to register a domain name for your Linode server.
NoteThis guide is written for a non-root user. Commands that require elevated privileges are prefixed withsudo. If you’re not familiar with thesudocommand, see the Linux Users and Groups guide.
Install Apache
Canvas uses Apache and Phusion’s Passenger to serve its web pages. Phusion has its own package repository, which this guide uses to install both Passenger and the Passenger module for Apache.
Add the key for the Phusion repository and HTTPS support for the package manager.
sudo apt install dirmngr gnupg sudo apt-key adv --keyserver hkp://keyserver.ubuntu.com:80 --recv-keys 561F9B9CAC40B2F7 sudo apt install apt-transport-https ca-certificatesAdd the Phusion repository and update the package manager. The
bionicin the first command corresponds to the code name for Ubuntu 20.04.sudo sh -c 'echo deb https://oss-binaries.phusionpassenger.com/apt/passenger bionic main > /etc/apt/sources.list.d/passenger.list' sudo apt updateInstall Apache, the Apache development headers, Passenger, and the Passenger module for Apache.
sudo apt-get install -y libapache2-mod-passenger sudo apt install -y apache2 apache2-dev passengerYou can check the Passenger version using the following command:
passenger -vEnable the Passenger and Rewrite for Apache.
sudo a2enmod passenger rewrite
Install PostgreSQL
Install PostgreSQL.
sudo apt-get install postgresqlCreate a Canvas user in PostgreSQL.
sudo -u postgres createuser canvas --no-createdb --no-superuser --no-createrole --pwpromptCreate a Canvas database, making the Canvas user its owner.
sudo -u postgres createdb canvas_production --owner=canvasMake the current user a PostgreSQL superuser.
sudo -u postgres psql -c "alter user $USER with superuser" postgres
Install Ruby
Canvas specifically requires version 2.6 of Ruby, which the default package repositories on Ubuntu do not have. However, Brightbox maintains a repository of Ruby versions for Ubuntu, which this guide makes use of to install the necessary version.
Add the Brightbox Ruby repository, and update the package manager.
sudo apt install software-properties-common sudo add-apt-repository ppa:brightbox/ruby-ng sudo apt updateInstall Ruby and its development components:
sudo apt-get install ruby2.6 ruby2.6-dev zlib1g-dev libxml2-dev libsqlite3-dev postgresql libpq-dev libxmlsec1-dev curl make g++Install Bundler, which Canvas uses for managing its Ruby libraries (“Gems”). Canvas specifically calls for version 2.1.4 of Bundler:
sudo gem install bundler --version 2.1.4
Install Node.js and Yarn
Install Node.js.
curl -sL https://deb.nodesource.com/setup_14.x | sudo -E bash - sudo apt-get install nodejs sudo npm install -g npm@latestInstall Yarn, a package manager used in the Canvas installation process.
curl -sS https://dl.yarnpkg.com/debian/pubkey.gpg | sudo apt-key add - echo "deb https://dl.yarnpkg.com/debian/ stable main" | sudo tee /etc/apt/sources.list.d/yarn.list sudo apt-get update && sudo apt-get install yarn=1.19.1-1
Install Canvas
Install Git, which is used to download the Canvas files from their repository. Using Git also makes it easier to update your Canvas installation in the future.
sudo apt-get install git-coreUse Git to download the Canvas repository.
git clone https://github.com/instructure/canvas-lms.git ~/canvasChange into the repository directory, and check out the latest stable branch of the repository.
cd ~/canvas git checkout stableCreate a directory for Canvas, copy the repository there, and change its ownership to the current user.
sudo mkdir -p /var/canvas sudo chown -R $USER /var/canvas sudo cp -R ~/canvas /varChange into the new Canvas root directory.
cd /var/canvasAll subsequent steps in this guide assume you are operating out of this directory unless stated otherwise.
Use Bundle to install Canvas’s Ruby dependencies.
bundle config set path 'vendor/bundle' bundle config set --local without 'pulsar' bundle installUse Yarn to install the necessary Node.js modules.
yarn install
Set Up the Canvas Configuration Files
Copy the example configuration files. Generally, the default configurations do not need to be modified, and the steps that follow walk you through the minor changes that are needed.
for config in amazon_s3 database delayed_jobs domain file_store outgoing_mail security external_migration; do cp config/$config.yml.example config/$config.yml; doneUsing your preferred text editor, open the database configuration file,
/var/canvas/config/database.yml. Modify theusernameandpasswordfields in theproductionsection to match thecanvasPostgreSQL user you created.- File: /var/canvas/config/database.yml
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9production: adapter: postgresql encoding: utf8 database: canvas_production host: localhost username: canvas password: password timeout: 5000
Open the domain configuration file,
/var/canvas/config/domain.yml. Modify thedomainfield in theproductionsection to match your server’s domain name.- File: /var/canvas/config/domain.yml
1 2 3 4production: domain: "example.com" ssl: true
Open the outgoing mail configuration file,
var/canvas/config/outgoing_mail.yml. Locate the production section, and complete it as follows.Enter the information for your SMTP service in the
address,port,user_name,password, andauthenticationfields.Enter your Canvas server’s domain name in the
domainfield.For
outgoing_address, create the email address from which Canvas is to deliver emails. Use your server’s domain name as the base of the address.In the
default_namefield, enter a name to be used by default on emails sent from Canvas.
- File: var/canvas/config/outgoing_mail.yml
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10production: address: "http://smtp.mailgun.org/" port: "587" user_name: "example-user" password: "password" authentication: "plain" domain: "example.com" outgoing_address: "canvas@example.com" default_name: "Example Canvas"
Open the security configuration file,
/var/canvas/config/security.yml. Enter a random string of 20 or more characters into theencryption_keyfield.You can use a command like the following to generate a random string, which you can then copy and paste into the configuration file. This example outputs a random string of 24 alphanumeric characters:
cat /dev/urandom | tr -dc 'A-Za-z0-9' | head -c 24; echo ''
Generate the Canvas Assets and Data
Create the required asset-related directories and files as shown in the following commands.
mkdir -p log tmp/pids public/assets app/stylesheets/brandable_css_brands touch app/stylesheets/_brandable_variables_defaults_autogenerated.scss touch Gemfile.lock touch log/production.logAssign ownership of key Canvas files to the current user.
sudo chown -R $USER config/environment.rb log tmp public/assets app/stylesheets/_brandable_variables_defaults_autogenerated.scss app/stylesheets/brandable_css_brands Gemfile.lock config.ruRun the Yarn installer again.
yarn installUse the Bundle to rehash the encryption key and compile Canvas’s assets.
RAILS_ENV=production bundle exec rake db:reset_encryption_key_hash RAILS_ENV=production bundle exec rake canvas:compile_assetsObserve the commands’ output for any errors that stop the processes. If you encounter any, run the command again. The asset compilation can consume a lot of memory, so it may be helpful to stop any major processes running in the background. For instance, you can restart Apache before running these commands.
sudo systemctl restart apache2Assign ownership of the
brandable_cssdirectory to the current user.sudo chown -R $USER public/dist/brandable_cssUse the Bundle to generate the initial data for Canvas.
RAILS_ENV=production bundle exec rake db:initial_setupYou are prompted to enter an email address and password, which are used to create the Canvas administrator login. You are also prompted to enter a name for your Canvas site and to select your preference for sending usage data to Canvas.
Assign ownership of the configuration files to the current user, and limit them to read access.
sudo chown $USER config/*.yml sudo chmod 400 config/*.ymlUse the following commands to set up and start the automated jobs the Canvas application relies on.
sudo ln -s /var/canvas/script/canvas_init /etc/init.d/canvas_init sudo update-rc.d canvas_init defaults sudo /etc/init.d/canvas_init start
Configure Apache for Canvas
Remove the default Apache site configuration.
sudo unlink /etc/apache2/sites-enabled/000-default.confUsing your preferred text editor, create and open a new configuration file,
/etc/apache2/sites-available/canvas.conf. Enter the following as the file’s content. Replaceexample@example-email.comwith the email address for the system administrator.- File: /etc/apache2/sites-available/canvas.conf
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38<VirtualHost *:80> ServerName example.com ServerAlias example.com ServerAdmin example@example-email.com DocumentRoot /var/canvas/public RewriteEngine On RewriteCond %{HTTP:X-Forwarded-Proto} !=https RewriteCond %{REQUEST_URI} !^/health_check RewriteRule (.*) <https://%{HTTP_HOST}%{REQUEST_URI>} [L] ErrorLog /var/log/apache2/canvas_errors.log LogLevel warn CustomLog /var/log/apache2/canvas_access.log combined SetEnv RAILS_ENV production <Directory /var/canvas/public> Allow from all Options -MultiViews </Directory> </VirtualHost> <VirtualHost *:443> ServerName example.com ServerAlias example.com ServerAdmin example@example-email.com DocumentRoot /var/canvas/public ErrorLog /var/log/apache2/canvas_errors.log LogLevel warn CustomLog /var/log/apache2/canvas_ssl_access.log combined SSLEngine on BrowserMatch "MSIE [17-9]" ssl-unclean-shutdown SSLCertificateFile /etc/ssl/certs/ssl-cert-snakeoil.pem SSLCertificateKeyFile /etc/ssl/private/ssl-cert-snakeoil.key SetEnv RAILS_ENV production <Directory /var/canvas/public> Options All AllowOverride All Require all granted </Directory> </VirtualHost>
Open the Passenger configuration file,
/etc/apache2/mods-available/passenger.conf. Add aPassengerDefaultUserline, and make its value the username of the user you used to set up Canvas. This isexample-userin the following example.- File: /etc/apache2/mods-available/passenger.conf
1 2 3 4 5 6<IfModule mod_passenger.c> PassengerRoot /usr/lib/ruby/vendor_ruby/phusion_passenger/locations.ini PassengerDefaultRuby /usr/bin/passenger_free_ruby PassengerDefaultUser example-user </IfModule>
Note
Canvas has a relatively long startup time, which can sometimes lead to timeout issues. You can add a version of the following line to the
passenger.conffile to increase the time before Canvas times out at startup. This example increases the amount of time before Passenger times out, from the default 60 seconds up to 180 seconds:PassengerStartTimeout 180Allow HTTP and HTTPS connections on the system’s firewall.
sudo ufw allow http sudo ufw allow https sudo ufw reloadEnable the Apache site configuration.
sudo a2ensite canvasRestart Apache for the changes to take effect.
sudo systemctl restart apache2
Set Up an SSL Certificate
By default, your Canvas site uses self-signed SSL certificates. The following steps show you how to use Certbot to request and download a free certificate from Let’s Encrypt.
Update the Snap app store. Snap provides application bundles that work across major Linux distributions and comes by default with all Ubuntu releases since 16.04.
sudo snap install core && sudo snap refresh coreRemove any existing Certbot installation.
sudo apt remove certbotInstall Certbot.
sudo snap install --classic certbotDownload a certificate for your site. When prompted, select your site’s domain name from the list of configured Apache domains.
sudo certbot certonly --apacheCertbot includes a Chron job that automatically renews your certificate before it expires. You can test the automatic renewal with the following command.
sudo certbot renew --dry-runOpen the
/etc/apache2/sites-available/canvas.conffile again, and modify theSSLlines as follows.- File: /etc/apache2/sites-available/canvas.conf
1 2 3SSLCertificateFile /etc/letsencrypt/live/example.com/fullchain.pem SSLCertificateKeyFile /etc/letsencrypt/live/example.com/privkey.pem
Enable the SSL module.
sudo a2enmod sslRestart the Apache server.
sudo systemctl restart apache2
Install Redis
Canvas has caching disabled by default, but you can, optionally, configure it to use Redis for caching. The following steps show you how to install Redis and configure Canvas to use it.
Add the Redis repository, and update the package manager.
sudo add-apt-repository ppa:chris-lea/redis-server sudo apt-get updateInstall Redis.
sudo apt-get install redis-serverCopy the example cache configuration file. This and the following commands assume you are again in the Canvas root directory (
/var/canvas).sudo cp config/cache_store.yml.example config/cache_store.ymlUsing your preferred text editor, open the
cache_store.ymlfile, and setredis_storeas thecache_storefordevelopment,test, andproduction. The configuration file should resemble the following:- File: /var/canvas/config/cache_store.yml
1 2 3 4 5 6 7development: cache_store: redis_store test: cache_store: redis_store production: cache_store: redis_store
Copy the example Redis configuration file.
sudo cp config/redis.yml.example config/redis.ymlOpen the
redis.ymlfile. Add aproductionsection like the following, entering the server location for Redis. If you are running Redis on the same machine as Canvas, this should beredis://localhost, as in the following example:- File: /var/canvas/config/redis.yml
1 2 3 4production: servers: - redis://localhost
Once again assign ownership of the configuration files to the current user and limit them to read access.
sudo chown $USER config/*.yml sudo chmod 400 config/*.ymlRestart Apache for the changes to take effect.
sudo systemctl restart apache2
Next Steps
You have successfully gotten your Canvas website up and running. Visit the site by navigating to your server’s domain name in a web browser. You are prompted to log in, which you can do using the Canvas administrator credentials you created earlier.
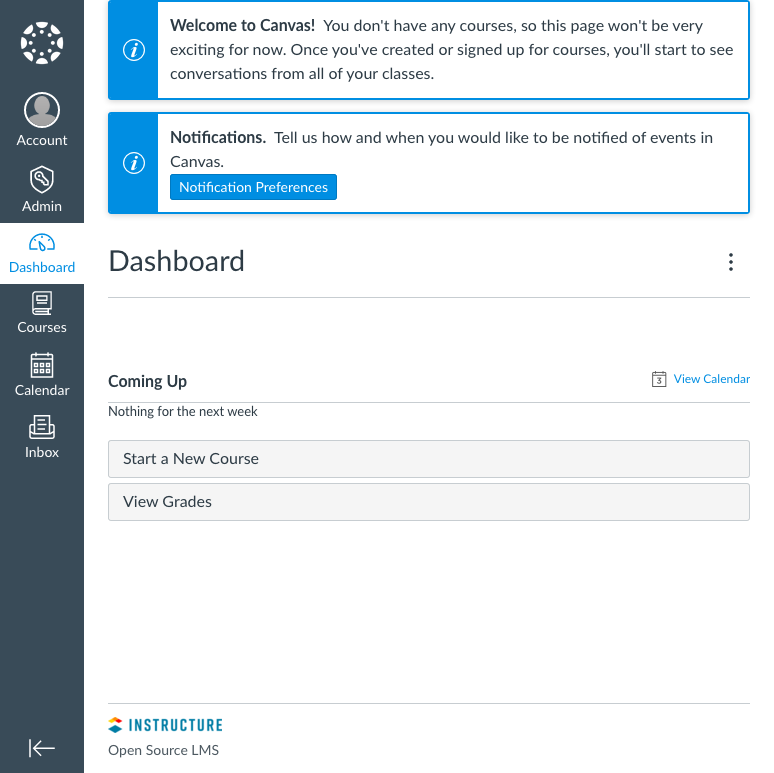
Once you log in, you are taken to your Canvas dashboard, from which you can view, create, and manage your Canvas website’s content.
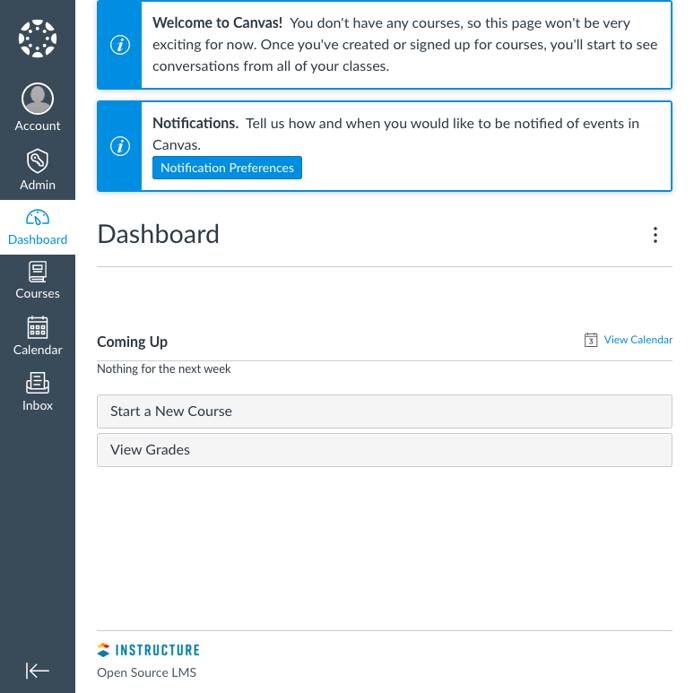
You can learn more about how to get started using your Canvas website and all the features it has to offer on the Canvas Community website. Be sure to check out the wealth of guides the Canvas Community has, covering everything from basic, day-to-day usage to advanced features.
More Information
You may wish to consult the following resources for additional information on this topic. While these are provided in the hope that they will be useful, please note that we cannot vouch for the accuracy or timeliness of externally hosted materials.
This page was originally published on